乙肝能治愈吗?
来源: 艾防中心
乙肝,全称为乙型肝炎,是由乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)感染机体后所引起的疾病。据估计,我国每20个人中就约有一个人感染HBV,且感染人群的年龄主要是30岁以上。慢性乙肝(CHB)如不及时治疗,可逐渐发展为肝硬化、肝功能衰竭甚至肝癌。有效的治疗可以抑制病毒复制,减少病毒对肝脏的损害,延缓疾病进展,降低肝硬化和肝癌的发生风险。抗病毒治疗是乙肝治疗的核心,通过使用核苷(酸)类似物(NAs)或干扰素等药物,可以有效地降低病毒载量,使患者的肝功能得到改善,肝脏炎症得到缓解。
乙肝能治愈吗?
随着医学研究的不断深入,乙肝治疗的目标已经从单纯的病毒抑制提升到了更高层次的"治愈"概念,目前临床上主要追求的是"功能性治愈"。
北京大学医学部庄辉院士指出,功能性治愈是指在停止抗病毒治疗后至少24周实现:乙肝表面抗原(HBsAg)降至0.05IU/mL以下,HBV DNA降至10IU/mL以下,HBeAg阴性(抗-HBe阳转),抗HBc阳性,ALT正常和肝组织学明显改善。这意味着病毒被有效控制,肝脏炎症得到缓解,患者发生肝硬化、肝癌的风险大大降低。
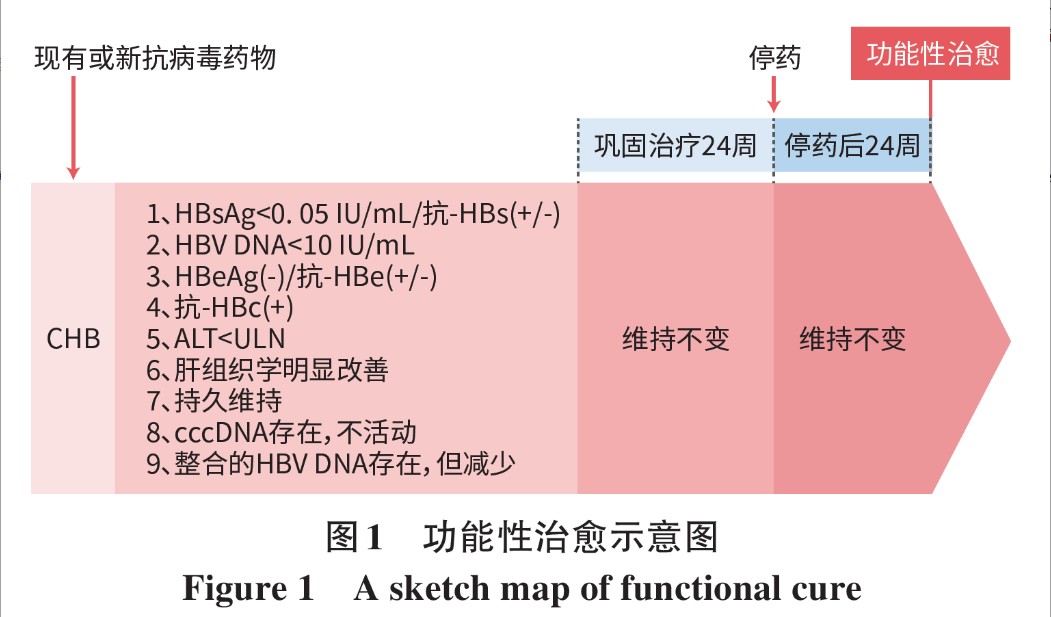
(引自:庄辉.慢性乙型肝炎功能性治愈不是梦[J].临床肝胆病杂志,41(1):2-6.)
怎样达到功能性治愈?
目前,对优势人群采取合适的治疗方案可以实现功能性治愈,第一种方案是:
在NAs治疗后,对优势人群加用或单用聚乙二醇干扰素α(PEG-IFN-α)治疗。优势人群需要满足:HBV DNA<10 IU/mL,HBeAg阴性(抗-HBe阳转), HBsAg<500 IU/mL和ALT正常。第二种方案是:应用NAs有限疗程,获得功能性治愈。NAs有限疗程的优势人群需要满足: HBsAg<100 IU/mL,HBeAg阴性(抗-HBe阳转),HBV DNA<10 IU/mL,ALT正常。此外,还有目前正处于临床试验的新药和联合治疗策略正在探索当中。
所以,我们有理由相信,未来将有更多的患者能够实现功能性治愈,随着医学研究的不断深入,乙肝的完全治愈也终将成为现实。
参考文献
1. 庄辉.慢性乙型肝炎功能性治愈不是梦[J].临床肝胆病杂志,41(1):2-6. DOI:10.12449/JCH250101.
2. LOK ASF. Toward a functional cure for hepatitis B[J]. Gut Liver,2024, 18(4): 593-601. DOI: 10.5009/gnl240023.
3.GHANY MG, BUTI M, LAMPERTICO P, et al. Guidance on treatment endpoints and study design for clinical trials aiming to achieve cure in chronic hepatitis B and D: Report from the 2022 AASLD-EASL HBV-HDV treatment endpoints conference[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79(5): 1254-1269. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.06.002.
4. LI MH, YI W, ZHANG L, et al. Predictors of sustained functional cure in hepatitis B envelope antigen-negative patients achieving hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance with interferon-alpha-based therapy [J]. J Viral Hepat, 2019, 26(Suppl 1): 32-41. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13151.
5. LI MH, SUN FF, BI XY, et al. Consolidation treatment needed for sustained HBsAg-negative response induced by interferon-alpha in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Virol Sin, 2022, 37(3):390-397. DOI: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.03.001.
6. YIP TCF, WONG GLH, WONG VWS, et al. Durability of hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in untreated and nucleos(t)ide analogue-treated patients[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68(1): 63-72. DOI:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.09.018.
7. LOK AS, ZOULIM F, DUSHEIKO G, et al. Durability of hepatitis B surface antigen loss with nucleotide analogue and peginterferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2019 ,4(1):8-20. DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1436.
8. YIP TCF, LOK ASF. How do we determine whether a functional cure for HBV infection has been achieved?[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(3): 548-550. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.033.
9. XIE C, LIN BL, XIE DY, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b promoted HBsAg loss in nucleos(t)ide analogue-treated patients: a large-scale real-world study (Everest Project)[J]. J Hepatol, 2026.
10. GAO N, GUAN GW, XU GL, et al. Integrated HBV DNA and cccDNA maintain transcriptional activity in intrahepatic HBsAg-positive patients with functional cure following PEG-IFN-based therapy[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2023, 58(10): 1086-1098. DOI: 10.1111/apt.17670.
11.HIRODE G, CHOI HSJ, CHEN CH, et al. Off-therapy response after nucleos(t)ide analogue withdrawal in patients with chronic hepatitis B: An international, multicenter, multiethnic cohort (RETRACT-B study) [J]. Gastroenterology, 2022, 162(3): 757-771. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.11.002.
12. LIM SG, TEO AE, CHAN ESY, et al. Stopping nucleos(t)ide analogues in chronic hepatitis B using HBsAg thresholds: A meta-analysis and meta-regression[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.05.040.
13. BLOCK PD, LIM JK. Unmet needs in the clinical management of chronic hepatitis B infection[J]. J Formos Med Assoc, 2024. DOI:10.1016/j.jfma.2024.08.020.
14. PETERS MG, YUEN MF, TERRAULT N, et al. Chronic hepatitis B finite treatment: Similar and different concerns with new drug classes [J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2024, 78(4): 983-990. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciad506.
15. HOU JL, ZHANG WH, XIE Q, et al. Xalnesiran with or without an immunodulator in chronic hepatitis B[J]. N Engl J Med, 2024, 391(22): 2098-2109. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2405485.
16. AGARWAL K, BUTI M, van BÖMMEL F, et al. JNJ-73763989 and bersacapavir treatment in nucleos(t)ide analogue-suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B: REEF-2[J]. J Hepatol, 2024, 81(3):404-414. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.03.046.
17. GOPALAKRISHNA H, GHANY MG. Perspective on emerging therapies to achieve functional cure of chronic hepatitis B[J]. Curr Hepatol Rep, 2024, 23(2): 241-252. DOI: 10.1007/s11901-024-00652-9.



 京公网安备 11011402013011号
京公网安备 11011402013011号